Big data — where to start
Professional directions in the world of Big Data
The term “big data” hides many concepts: from the information arrays themselves to technologies for their collection, processing, analysis and storage. Therefore, before trying to grasp the immensity in an effort to study everything that relates to Big Data, we highlight the following areas in this area of knowledge:
- analytics – formulation of hypotheses, visualization of information, search for patterns in the data set (dataset), preparation of information for modeling, development of machine learning algorithms (Machine Learning) and interpretation of their results. It involves analysts and data scientists, as well as machine learning specialists. In addition to tasks related directly to data science (Data Mining), sometimes analysts also perform duties on the analysis of the subject area and business processes (Business Intelligence). All this is necessary for a precise understanding of the customer’s needs to determine the independent variables that are needed to build analytical or predictive models.
- engineering – creation, configuration and support of hardware and software infrastructure for the collection, processing, analysis and storage of information flows and arrays, including the configuration of local and cloud clusters. The big Data administrator and engineer are responsible for these processes.
At the junction of the above 2 areas are programmer Big Data and DevOps-engineer, as well as a specialist in support of the life cycle of corporate data (DataOps) and data Director (CDO, Chief Data Officer), who oversees the enterprise all issues related to information.
Big data: where to start
Knowing how the work is generally divided between big data specialists, it becomes much easier to answer the main question of a newcomer in the world of Big Data “where to start”. Before you dive into the many tutorials on Apache Hadoop and machine Learning algorithms, you need to understand what attracts you more:
- application programming;
- admin;
- information flow architecture design and maintenance;
- data analysis;
- creation of mathematical models and algorithms of information processing.
In addition, it should be noted that, in addition to line specialists (programmers, administrators, engineers, architects), knowledge in the field of big data is also necessary for managers to see the possibilities of digitalization of their business and the potential benefits of its digital transformation. At the same time, the Manager does not need to know all the details, such as how Apache Kafka works. However, in order not to be a “teapot”, it is extremely useful for the Manager to navigate the industry scenarios of using Big Data (use-cases), to understand the ways of monetization of big data and the specifics of corporate digitalization in order to effectively spend time, labor and material resources, and not to expect more from technologies than they can give.
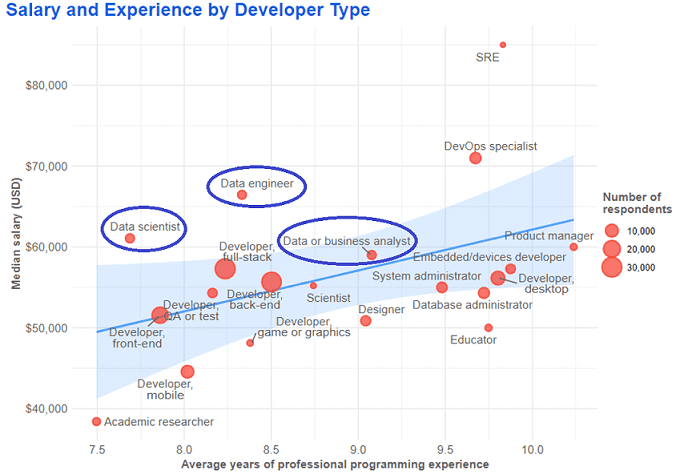
Image: Salaries of IT professionals in 2019 according to Stack OverFlow
As an additional motivation for studying Big Data, we note that professionals in this area earn the most among IT professionals. For example, in 2019, according to the annual Stack OverFlow study, the annual salary of analysts, engineers and data researchers in the USA was $60,000-70,000. Moreover, since digitalization is rapidly penetrating into all spheres of activity, from industry to education, the demand for data specialists is growing all over the world all the time. Thus, big data is a very promising and financially profitable area of IT.