Who is a Data Engineer at Big Data: the professional competence of engineer data
What a data engineer does
In order for Data Analyst and Data Scientist to extract business-useful knowledge from Big Data streams and arrays, all of this big data must be appropriately collected and stored. This is what Data Engineer does: it configures the infrastructure for Big Data, corporate data warehouses, ETL systems, internal databases and third-party sources (mail, CRM, ERP and other application systems).
Therefore, data engineer performs the following operations:
- organization of automated data collection from various sources in a single centralized storage (Data Warehouse) or Data Lake;
- handling and storage of the data arrays;
- set up, integrate, and create data marts for analysts and researchers;
- creation of regular and continuous data preparation pipelines (CI/CD pipelines);
- monitoring and improving data quality.

Image 1: Differences between Data Engineer and Data Scientist
Data Engineer professional skills: what Data Engineer should know
While Data Scientist and Data Analyst focusing on the essence of the information arrays Big Data engineer data organise infrastructure. To do this, he needs the following professional knowledge and skills:
- algorithms and data structures;
- principles of storing information in SQL and NoSQL, as well as the ability to work with relational and non-relational databases (MySQL, MSSQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, SQL Server, Oracle, HP Vertica, Amazon Redshift, etc.).)
- ETL systems (Informatica ETL, Pentaho ETL, Talend, etc.);
- cloud-based platform for Big Data solutions (Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud Platform, Microsoft Azure, and other similar solutions from major PaaS/IaaS providers);
- Apache Hadoop stack (HDFS, HBase, Cassandra) and SQL engines for analyzing data stored in distributed file systems such as HDFS (Apache Hive, Impala, etc.).);
- clusters of Big Data on the Apache (Hadoop, Kafka, Spark);
- programming languages (Python, Java, Scala) for working with Big Data systems.
Despite working closely with ETL and OLAP systems, the Data Engineer, unlike an analyst and data scientist, does not require expert knowledge of Business Intelligence (BI), as well as the specifics of the subject area. Experience with software development and cluster administration will be much more useful for a data engineer, although this is mainly the responsibility of the Big Data administrator.
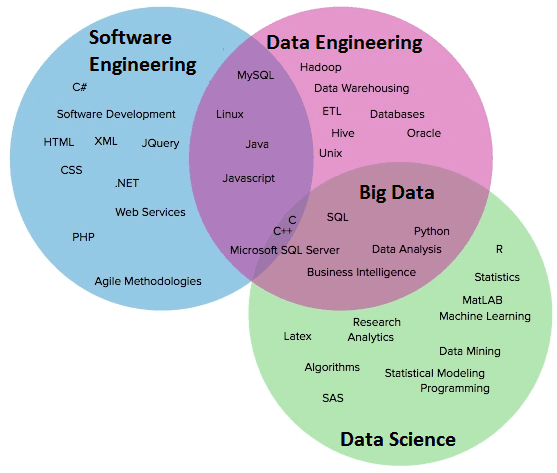
Image 2: Data Engineer Professional Areas
Salary and demand for a data engineer in the labor market
In the article Big Data where to start, speaking about professions in the world of big data, we already mentioned that IT specialists in this field are very highly valued in the labor market. At the same time, due to the total digitalization and digital transformation of various sectors of the economy, there is an increased demand for Data Professional’s.
With such a shortage of personnel, the salary of data engineers is one of the highest in IT. For example, according to the annual study of the Stack OverFlow portal, in 2019, the American Data Engineer earns about 66 thousand dollars a year. Not every Data Analyst or Data Scientist can boast of such earnings.
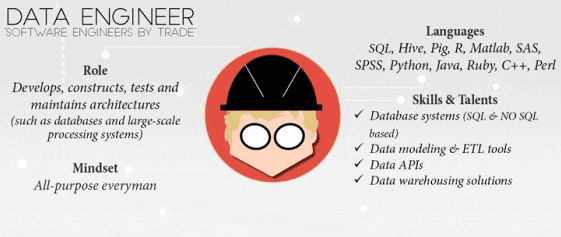
Image 3: Professional portrait of data engineer